
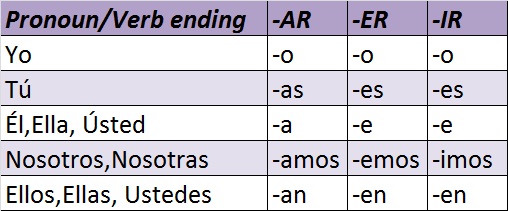
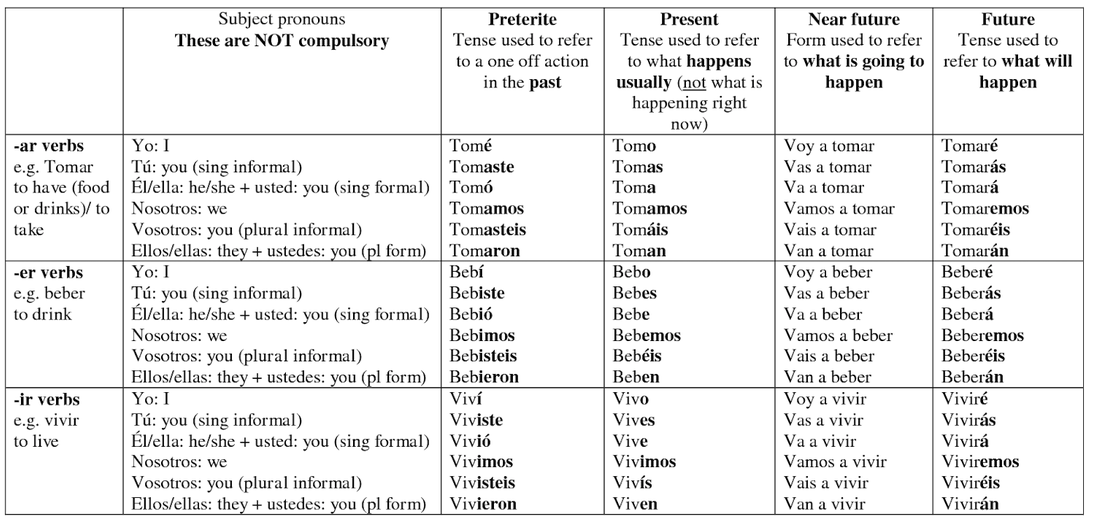
You need to use the past perfect tense for the translation in Spanish. Something had happened prior to something else The next thing you need to think about is finding the right time to throw the Spanish past perfect into conversation. When to use the Spanish past perfect tense If you can’t remember how to form a past participle check out this post.

Next, you need to form a past participle out of the verb you want to use. Here is a list of the past imperfect conjugations of haber: Person If you want to conjugate a verb in the the past perfect tense, you need two things: a past participle and a conjugation of the verb haber in the past imperfect tense. I had already finished my homework when my dad asked me to do it.Īs you can see, the word ‘already’ is important here because it tells you that one event is finished before another event starts.įor any event that finished prior to another event, you’ll need the Spanish past perfect to describe it. I had already woken up when my alarm sounded. …well, this is because the past perfect tense describes an event that occurs before another event. I mentioned earlier that you may have to combine the past perfect with the past simple or past imperfect… In other words, this tense is great for telling stories in Spanish. The past perfect tense, also known as el pretérito pluscuamperfecto, is really useful for describing a sequence of events in the past. So what is the past perfect tense in Spanish used for?
IR PAST PERFECT PDF
Printable Version: Download this PDF version of the rules for the Past Perfect Tense to use as a study reference.Ī quick introduction to the past perfect tense
IR PAST PERFECT HOW TO
So, in today’s post, you’ll learn when to use the Spanish past perfect tense, how to form it, and I’ll show you a few key phrases that will help you learn this tense quickly. Moreover, while researching this post I realised that one Spanish phrase conjugated in the past perfect occurs more frequently than ‘ otra vez‘ or ‘ se llama‘ in conversational Spanish. In fact, you’ll only need to focus on a few really common phrases to get a strong feel for this tense. You may also be tempted to use the present perfect when you really should be using the past perfect.īut, that doesn’t mean you can’t quickly learn how to use this tense properly. This is because you’ll often have to use the past perfect with other tenses such as the past simple or past imperfect. I 'd never met anyone from California before I met Jim.ĭo this exercise to test your grammar again.The Spanish past perfect is definitely not the easiest tense to use. Had you ever visited London when you moved there? It was the most beautiful photo I 'd ever seen. I went to visit her when she'd just moved to Berlin. It still hadn't rained at the beginning of May. I called his office but he'd already left. We often use the adverbs already (= 'before the specified time'), still (= as previously), just (= 'a very short time before the specified time'), ever (= 'at any time before the specified time') or never (= 'at no time before the specified time') with the past perfect. Sadly, the author died before he'd finished the series. We can also use before + past perfect to show that an action was not done or was incomplete when the past simple action happened. (NOT The Romans had spoken Latin.) Past perfect after before Note that if there's only a single event, we don't use the past perfect, even if it happened a long time ago. The thief had escaped when the police arrived. The following sentence has the same meaning. It doesn't matter in which order we say the two events. When the police arrived, the thief had escaped. The past perfect shows the earlier action and the past simple shows the later action. We can use the past perfect to show the order of two past events. Had the parcel arrived when you called yesterday? Past perfect for the earlier of two past actions We'd finished all the water before we were halfway up the mountain. She'd published her first poem by the time she was eight. We use the past perfect simple ( had + past participle) to talk about time up to a certain point in the past. Grammar explanation Time up to a point in the past My new job wasn't exactly what I’d expected. The hotel was full, so I was glad that we'd booked in advance. He couldn't make a sandwich because he'd forgotten to buy bread. Look at these examples to see how the past perfect is used.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
