
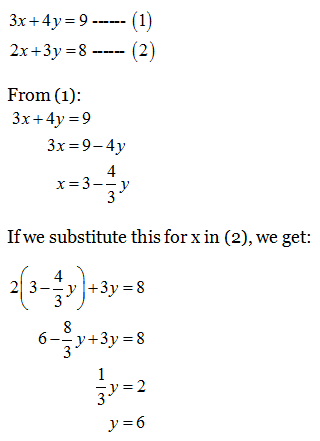
The nine simultaneous equation solver was one of Japan’searly large-scale computing device and is on permanent exhibit at the National Museum of Science and Nature. By moving the bar and reading the tape’s length, the equations’ solution could be found. The angle represented an unknown value, and the length of the steel tape attached to the bar’s pulley represented an equation. The nine simultaneous equation solver had brass bars with variable angles attached to steel pulleys. A nine-dimensional simultaneous equation is generally a set of nine linear equations with one known value and nine unknown values. The Aviation Laboratory’s machine had the same construction as Wilbur’s simultaneous calculator and could also solve nine-dimensional simultaneous equations. The computer was enormously useful in civil engineering structural analysis and calculating matrices for economics. This large, analog computer could solve up to nine simultaneous equations to within one percent accuracy by varying the length of belts by changing the angle of brass bars. Wilbur had participated in Vannevar Bush’s computing project at MIT in 1934 and taking the idea of using a machine to solve algebraic equations, he completed his mechanical calculator in 1936. The nine simultaneous equation solver was developed based on mechanical calculator for solving simultaneous equations created by MIT professor John Wilbur.

First generate the question, then work them out and check with the answer.Sasaki Tatsujiro, Shiga Makoto, Miita Junichi, and others from Tokyo Imperial University’s Aviation Laboratory built the nine simultaneous equation solver in 1944, one of Japan’s early large-scale mechanical calculator. AJmain, hard maths equations, variables and exponents, equation worksheets solving for y, factoring in alegebra, answer to glencoe algebra 1.
#Simultaneous equation solver free#
You can generate as many questions as you want with the following programme, along with the answers. Simultaneous equations calculator substitution method, rules of simplifying radical expressions, free intermediate algebra worksheets, real life situations dealing with rational expressions. Now, in order to complement what you have just learnt, work out the following questions: The method can be extended to solve any pair simultaneous equations all you have to do is rearranging them in matrix form. The following image clearly shows how it is done. Then, matrix, Q, which gives the values of x and y could be found by matrix multiplication. In this method, the inverse matrix of the matrix P must be found first. It is useful for advanced mathematics too. Matrices is part of Further Mathematics Syllabus.

This is ideal for those who do Further Mathematics(FP1) at A-Level. The coordinates of the point of intersection are x = 3 and y = 2. Rearrange the two equations in the form of y = mx + c and draw two lines for them on the same grid. The coordinates of this point are the solutions of the equations.

Then the point where the two lines intersect at is noted. In this method, two straight lines are drawn for each equation. We get y in terms of x or vice versa from one equation, and put that in the other. In this case, to eliminate y, the first equation must be multiplied by 2 and the second equation must be To remove y, multiply the first equation by 2 and then add the two equations together. If we add the two equations, we can remove y. In this method, we must get rid of one variable in order to find the other. That way, it is possible to find the values that. We use three different methods to solve simultaneous equations. Therefore, to solve an equation with two or more variables, other equations are needed to be used alongside it. Generate random simultaneous equations along with answers - for practiceĮquations that must be solved at the same time are simultaneous equations.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
